May 2021
On-Call Remote Monitoring Disaster
Zara Patterson
Highly Specialised Cardiac Physiologist – Leeds Teaching Hospitals
Sunaina Asghar
Trainee Device Physiologist — Leeds Teaching Hospitals
Disclosure: The author has no conflict of interests to declare.
Background
A 78-year-old male underwent an elective battery replacement of an Abbott CRT-D. He has a background history of ischemic heart disease (IHD), NYHA class II heart failure (HF) symptoms, sinus rhythm with complete heart block and previous appropriate anti-tachycardia pacing (ATP) therapies for monomorphic ventricular tachycardia.
Implanted leads included;
RA Lead: Medtronic Select Secure Sense
RV Lead: SJM Durata 7120Q
LV Lead: SJM Quicksite 1058T
10 weeks post battery replacement an unscheduled remote alert was received for ‘RV lead impedance measurement out of range’. The right ventricular (RV) lead impedance trend is displayed in Figure 1.
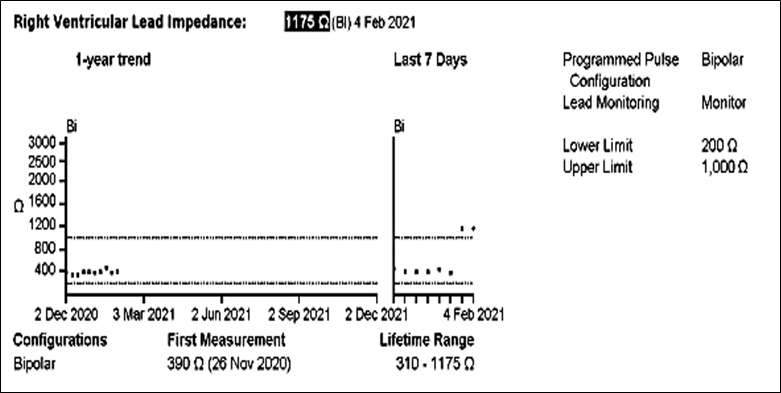
Figure 1 – RV lead impedance trend displaying recorded impedance measurements and range since elective battery replacement.
QUESTION 1
What action is required?
10 days following the face-to-face check…
10 days following the face to face check the on-call cardiac physiologist received another Merlin remote alert, this time for ‘ATP delivery and aborted shock’ Transmission details and relevant electrograms are displayed in Figures 2a-b.
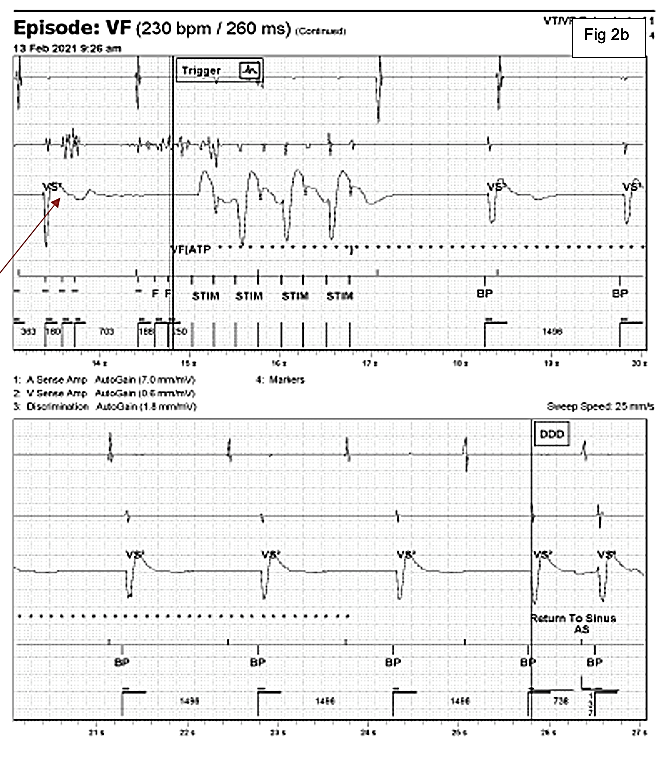
Figure 2a-b: Automatic Merlin.net alert transmission for ATP delivery and aborted shock. Channels displayed top to bottom, include the atrial EGM (A sense amp), right ventricular near field EGM (V sense amp), the far field discrimination channel and marker channel.
EGM Description
The EGM shows an episode of noise which receives an inappropriate ATP therapy. At the start of the trace in Figure 2a the EGM shows an atrial sense (As) biventricular paced (BP) rhythm. There is then a sudden change on the near field RV channel with high frequency noise signals detected which the device detects as ventricular events falling in the VF detection zone. These events are marked with an F for fibrillation sensing. At the end of the 12th F marker, ATP is delivered, marked as STIM on the trace. At the same time the device starts to charge (star markers). When the star markers are no longer displayed the device is charged ready to deliver a shock. The shock is then fortunately aborted with the disappearance of the high frequency noise signals on the near field channel and a return to sinus marker declares the end of the episode.

